Port and Starboard: A Guide

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContents
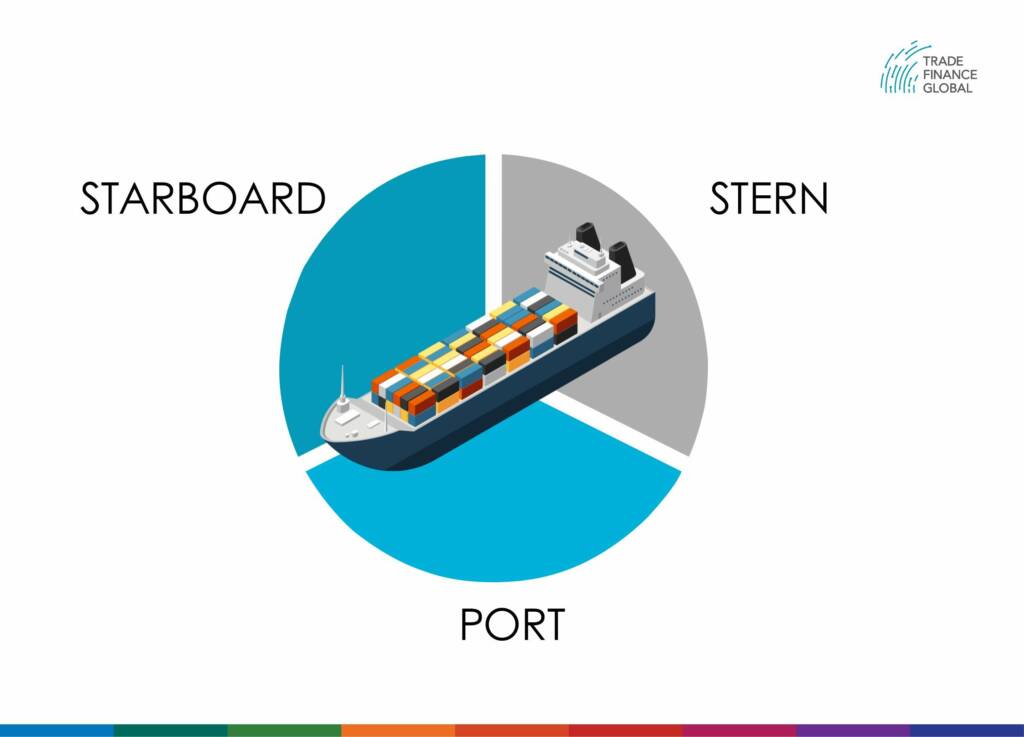
Port and starboard are nautical terms that refer to the left side and right side of a ship, but only in relation to the bow (the front of a ship) and the stern (the rear of a ship).
Why are the terms port and starboard used?
The reason that port and starboard are used instead of left and right is simple: when you’re on a ship, the meaning of the words ‘left side’ and ‘right side’ of the ship can change based on the position of the speaker and the listener.
Consequently, sailors needed a pair of words that could denote the right or left side of the ship regardless of their position, so they introduced the terms port and starboard.
The terms port and starboard have a long history in seafaring, from the invention of the steering oar to the issuance of International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs).
So, how did port and starboard come into being, and when exactly did sailors start using this system?
A nautical history lesson
To understand where the terms port and starboard come from, it’s useful to know a little bit about how ships have evolved over time.
Before the days of oil-powered or even coal-powered marine engines, ships used a mixture of wind sails and oars to propel themselves through the water.
Steering a wind-powered or oar-powered vessel was always tricky, but even more so for larger vessels carrying heavy loads of cargo.
To solve this problem, the prehistoric Egyptians invented a new kind of oar – a steering oar – which they placed at the stern of their vessels.
The exact date of this invention is unclear, but we know it happened long before the emergence of Ancient Egyptian civilization, which took place under Narmer, the first pharaoh, around 3100 BC.
Thankfully, however, the Ancient Egyptians gave us a much clearer than their ancestors of what these early steering oars would have looked like.
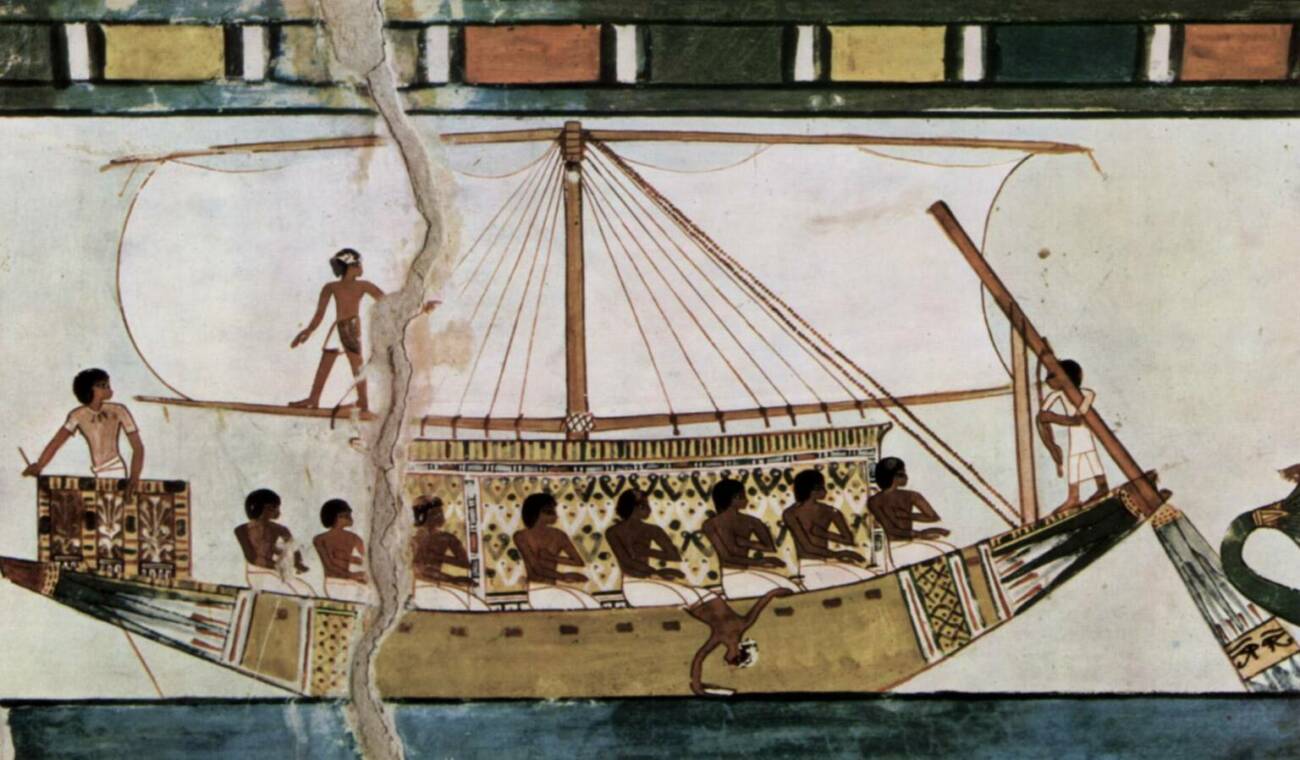
Here is a picture of a stern-mounted steering oar on an Egyptian riverboat, as depicted in the Tomb of Menna, which dates back to around 1422 – 1411 BC.

Evolution in motion – from steering oar to rudder
As we can see from the image above, the Ancient Egyptians simply propped up the steering oar and dangled it over the stern to steer the boat.
Over time, sailors would perfect the positioning of the steering oar, until eventually it evolved into what we know today as the rudder – but that took our ancestors a rather long time to figure out.
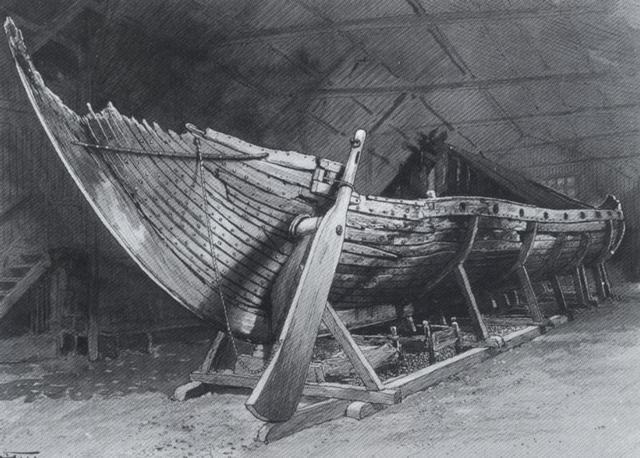
The Vikings, for example, used a specialised steering oar that could be attached to the stern of the ship.
This hi-tech oar – for its time – would have been used by the Vikings to guide them on their many raiding missions from Scandinavia to England.
But this still doesn’t explain where the words port and starboard come from.
A right-hand man’s world
To answer this question, we must first consider the best place to put the steering oar.
From a hydraulic perspective, the helmsman would obviously want to be holding the steering oar with his strongest hand.
And since nine out of 10 people are right-handed – according to science’s best estimates – then it made sense to put the steering oar on the right-hand side of the boat.
In the English language, then, it was simply this coincidence that led to the use of the terms ‘port’ and ‘starboard’.

To coin a phrase
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the word ‘starboard’ is derived from the Old English stēorbord.
Stēor means to ‘steer’, and bord means ‘side’.
Moreover, stēor is derived from the Old English stīeran, which is of Germanic origin, and is related to the Dutch sturen and German steuern.
As the Oxford dictionary explains, the English adopted this terminology from the early Teutonics (medieval Germans), whose “vessels were steered with a paddle over the right side.”
Conversely, the left-hand side of the boat became known as the ‘port’ side, as that would be the side of the boat used when docking in port.
This was essential at the time, to avoid catching or crushing the starboard steering oar.
What are port and starboard used for today?
In the early 13th century, a new invention started to spread among the seafaring peoples of Europe.
It was called the sternpost-mounted rudder, and it revolutionised not only the way ships sailed, but also how they docked at port.

Slowly, the rudder began to replace the steering oar, and this meant that ships no longer had to dock on the port side.
Clearly, the invention of the rudder brought a great deal of flexibility to shipping, but it did not mean that port and starboard immediately went out of use.
For one thing, port and starboard were still essential terms used by sailors to orient themselves on the boat.
But more importantly, as ships grew ever larger, and collisions grew ever more costly, port and starboard became essential terms for sailors on separate vessels to communicate with each other.
Port and starboard go electric
Following the discovery of electricity in 1752 by Benjamin Franklin, port and starboard could soon be expressed in the universal language of coloured lights.
In the 19th century, shipping companies began using a mix of red and green lights to indicate the port and starboard side of their vessels.
For example, in 1834 the City of Dublin Steamship Company started using white masthead lights, green starboard lights, and red port side lights.
But in 1836, the P&O Company of Southampton began using green port navigation lights, and a mixture of red and green lights on the starboard side.
This confusion continued until the Steam Navigation Act of 1846, which decreed that all British vessels must use red lights for the port side and green lights for the starboard.
This system was then adopted by Prussia in 1853, and France, Austria, and Hungary in 1858.
Later, in 1889, the United States convened the world’s first international maritime conference in Washington DC, where a further 27 seafaring nations signed up to Britain’s red-green system, which became effective in 1897.
This agreement formed an early prototype of today’s International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, or COLREGs for short.

Modern COLREGs and global shipping
First agreed upon in 1972, and in force since 1977, the COLREGs are a set of nautical rules devised by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
The IMO is a United Nations (UN) agency that was formed in 1948, and today it has 174 member states and three associate members, all of which must abide by the COLREGs.
Not only must IMO members use the red-green “sidelight” system devised by the British, but they must also use white lights on the masthead and stern.
This combination of red, white, and green makes it easier to identify a ship’s direction at night, and also makes it easier for ships to navigate in dangerous situations such as head-on, crossing, overtaking.
For example, Rule 14 of the COLREGs sets out how vessels should navigate in a head-on situation:
(a). When two power-driven vessels are meeting on reciprocal or nearly reciprocal courses so as to involve risk of collision, each shall alter her course to starboard so that each shall pass on the port side of the other.
And Rule 15 sets out how vessels should navigate in a crossing situation:
When two power-driven vessels are crossing so as to involve risk of collision, the vessel which has the other on her own starboard side shall keep out of the way and shall, if the circumstances of the case admit, avoid crossing ahead of the other vessel.
These are just a few examples of how port and starboard are used in today’s COLREGs, but you can find many more examples if you read the full text.
If you are interested in browsing the COLREGs, you will notice that the full text consists of 41 rules divided into six sections:
Part A
General
Part B
Steering and Sailing
Part C
Lights and Shapes
Part D
Sound and Light signals
Part E
Exemptions
Part F
Verification of compliance with the provisions of the Convention
If you are unsure about how COLREGs affect you and your business, you can get in touch with our distinguished team of experts using the link below.
- All Topics
- Key Terms
- Incoterms Resources
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences















