Trade and export finance providers and lender types | 2024 trade finance guide

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContents
What are the types of trade finance lenders?
Trade finance providers can broadly be split into banks and non-bank lenders (funds and alternative financial institutions).
When accessing trade finance, it is crucial that business owners choose a suitable lender among the different types of trade service providers on the market.
1. Banks
Banks account for the majority of financial institutions globally, although they range in size from small regional operators to large multinationals.
Banks are a popular source of trade finance because their cost of borrowing is often lower than most alternative lenders.
However, a bank is usually under heightened regulatory pressure, so there are longer decision timeframes and less flexibility.
The specific trade finance services that banks offer will vary, but will usually include services such as issuing bills of exchange or letters of credit and accepting drafts and negotiating notes.
Two main types of banks provide trade finance: large corporate and investment banks (CIBs) and smaller commercial banks.
The main difference between CIBs and smaller commercial banking is the size of the clients, with CIBs generally serving larger clients and larger transactions, while commercial banks tend to cater to a wider range of smaller clients.
Corporate and investment banks (CIBs)
These banks typically manage larger clients and transactions, and their strong global reputation means that they can provide cross-border services at a lower cost than smaller banks.
Some larger commercial banks also have specialised trade finance divisions that offer trade services and debt facilities.
Commercial banks
Smaller domestic banks can be advantageous to SMEs because their financial products may be more flexible and tailored to specific niche categories and verticals.
As with any bank, however, heightened regulatory pressures can make their decision-making process more time-consuming and less flexible.

Alternative finance providers and non-bank lenders
These lenders tend to be unregulated, which means their processes are often faster than traditional banks.
However, because many of them raise funding from sources such as banks, private investment, and crowd-funded (pooled) investment, the cost of the finance they offer can be significantly higher.
New technologies and platforms have been developed to disrupt the traditional lengthy application processes for trade finance products – including risk assessment, documentation to importers and exporters and supply credit.
Examples of alternative providers include development finance institutions (DFIs) and export credit agencies (ECAs).
Development finance institutions (DFIs)
Also known as development banks or development finance companies (DFCs), these institutions typically provide finance as a way to generate or promote economic development.
Often this is for mid-to-long-term projects, such as in the agricultural or mining sectors.
DFIs usually operate as joint ventures in emerging markets, where they encourage investment and provide insurance and guarantees against political and socio-economic risks.
They can also supply standby letters of credit (SBLCs), invoice discounting facilities, and project finance.
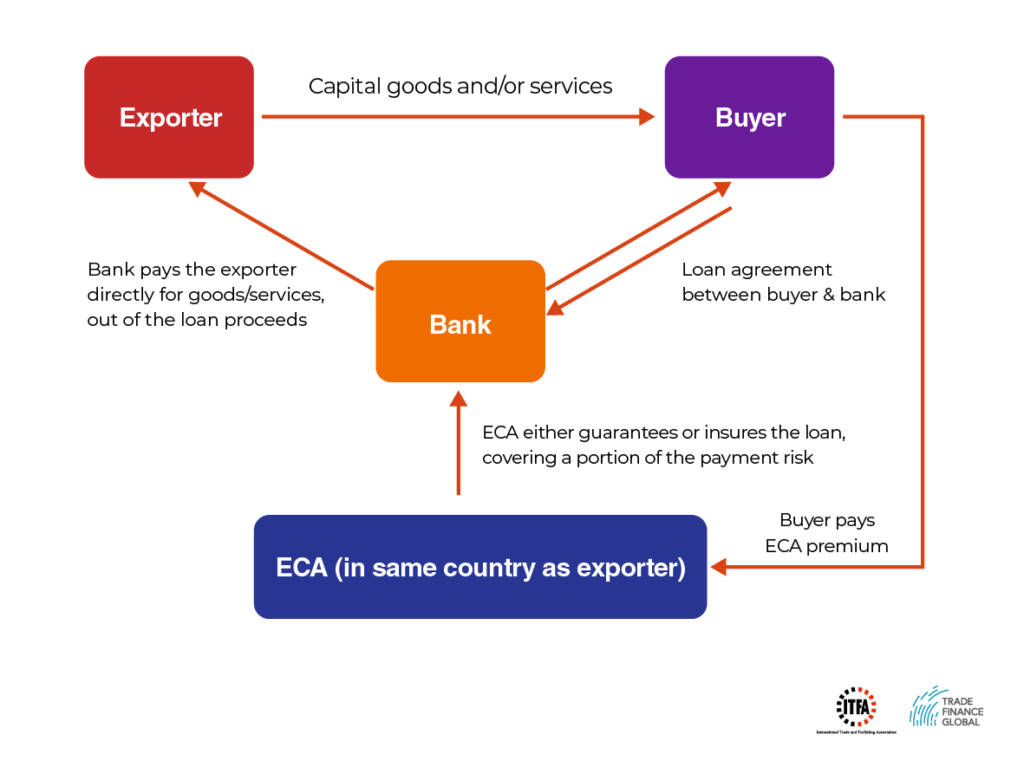
Export credit agencies (ECAs)
These are government-backed institutions – like UK Export Finance (UKEF) in the UK or Export Development Canada (EDC) in Canada – that guarantee a domestic company’s exports.
They tend to structure their finance and insurance around non-conventional risks, such as overseas commercial liabilities and political risk.
Find out more about the different ECAs around the world on our ECA hub.
Speak to our trade finance team
Our trade finance partners
- Trade Finance Resources
- All Trade Finance Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences
- Products we finance




















