Importing from Belgium


Belgium Country Profile
Official Name (Local Language) Royaume de Belgique; Koninkrijk Belgie
Capital Brussels
Population 11,409,077
Currency Euro
GDP $470.2 billion
Languages Euro
Phone Dial In 32
Belgium Exports Profile
Exports ($m USD) 429,98
Number of Exports Products 4,466
Number of Exports Partners 230
Belgium Economic Statistics
Government Website | https://www.belgium.be/en |
| Sovereign Ratings | https://countryeconomy.com/ratings/belgium |
| Central Bank | Nationale Bank van Belgie – Banque Nationale de Belgique |
| Currency USD Exchange Rate | 0.9214 |
| Unemployment Rate | 8.4% |
| Population below poverty line | 15.1% |
| Inflation Rate | 1.6% |
| Prime Lending Rate | 0.25% |
| GDP | $470.2 billion |
| GDP Pro Capita (PPP) | $44,900 |
| Currency Name | Euro |
| Currency Code | EUR |
| World Bank Classification | Upper Middle Income |
| Competitive Industrial Performance | 17/138 |
| Corruption Perceptions Index | 16/180 |
| Ease of Doing Business | 45/190 |
| Enabling Trade Index | 10/136 |
Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedImporting from Belgium
The western European country of Belgium is divided into three regions (Brussels-capital region, Flanders, and Wallonia) and three primary language groups (Dutch, French, and German).
Belgium is considered a small, open economy with over 11.5 million inhabitants and a GDP per capita of $44,500, as of 2020.
Over half of all banking transactions in the country are international financial transactions, owing to the volume of international business done.
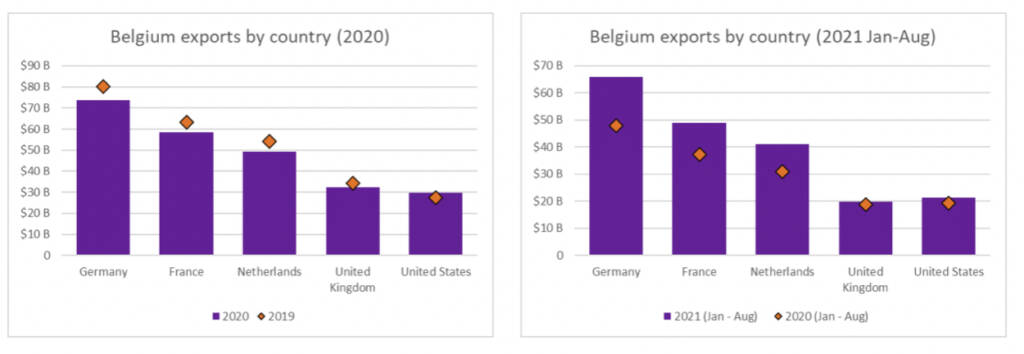
In 2019 the country sent out over $445 billion, primarily to Germany, France, the Netherlands, the UK, and the USA.
Of this, four key sectors accounted for over 57% of total Belgian exports.
These were; chemical products (26%), vehicles and transport equipment (12.7%), machinery and electrical equipment (10.6%), and base metals (8.2%).
Belgian SMEs comprise a much larger proportion of the nation’s total trade volumes.
Cumulatively, they account for nearly 70% of the country’s export value and more than 70% of its import value, compared to an average of around 40% and 50% respectively across all other Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) nations.
Importing from Belgium: What is trade finance?
Belgium is the thirteenth largest export economy.
It exports over $380B and imports around $470B, so there is a relatively large negative trade balance.
When conducting business internationally, firms in Belgium have access to a wide and flexible range of loan products offered by the 106 domestic and foreign banks that service the country.
Furthermore, over half of all banking transactions in the country are international financial transactions, owing to the volume of international business done.
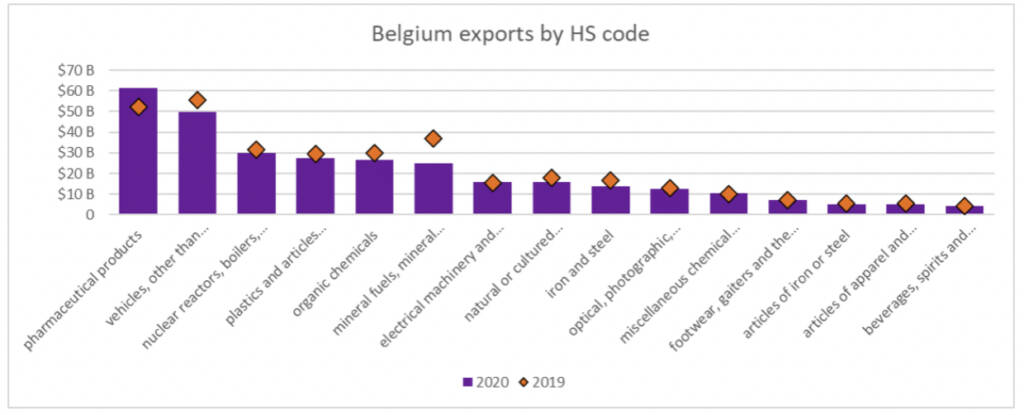
Chart Showing GDP Growth Compared to rest of world
GDP Composition for Belgium
Agriculture
0.6%
Sugar beets, fresh vegetables, fruits, grain, tobacco; beef, veal, pork, milk
Industry
21.8%
Engineering and metal products, motor vehicle assembly, transportation equipment, scientific instruments, processed food and beverages, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, base metals, textiles, glass, petroleum
Services
77.6%
Map
Top 5 Exports Partners
| Country | Trade | % Partner Share |
| Germany | 71,403 | 16.61 |
| France | 64,007 | 14.89 |
| Netherlands | 51,629 | 12.01 |
| United Kingdom | 36,217 | 8.42 |
| Italy | 21,097 | 4.91 |
Top 5 Exports Products
| Export Product | Number |
| Petroleum oils, etc, (excl. crude); preparation | 7.7% |
| Other medicaments of mixed or unmixed products, | 6.2% |
| Automobiles with diesel engine displacing more | 5.9% |
| Diamonds non-industrial unworked or simply sawn | 3.5% |
| Human and animal blood; microbial cultures; tox | 3.3% |
Local Partners
- All Topics
- Belgian Trade Resources
- Export Finance and ECA Topics
- Local Conferences



















