Artificial Intelligence

Access trade, receivables and supply chain finance
We assist companies to access trade and receivables finance through our relationships with 270+ banks, funds and alternative finance houses.
Get StartedContent
Artificial Intelligence
While big data analytics compile useful data for humans to use in decision-making, artificial intelligence (AI) is able to further process that data and produce an actual decision. According to the Encyclopedia Britannica, AI is:
“the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings. The term is frequently applied to the project of developing systems endowed with the intellectual processes characteristic of humans, such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize, or learn from past experience.”
AI is a broad term that is used to describe a series of subfields, such as machine learning, neural networks, deep learning and natural language processing (see Box 1).
Big data analytics and AI are closely linked. The development of big data analytics involves many AI theories and methods and therefore depends on AI, and the development of AI relies on big data analytics because it requires lots of data for the process of “learning”. As a result, many of the benefits and challenges for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) that big data analytics represent will also be represented by AI. The following sections will focus exclusively on the benefits and challenges that are unique to AI.
Box 1: Sub-categories of AI
Machine learning (ML): A subset of AI techniques that uses experience to improve performance.
Neural networks: Virtual network structures that are designed, in their topology and behaviour, to resemble neuron cells and the connections of the latter within the biological brain.
Deep learning: A subset of ML that uses multi-layered neural networks to solve complex problems.
Natural language processing (NLP): A branch of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and humans using natural language, i.e. naturally evolved human language, as opposed to binary computer language.
Potential benefits for MSMEs
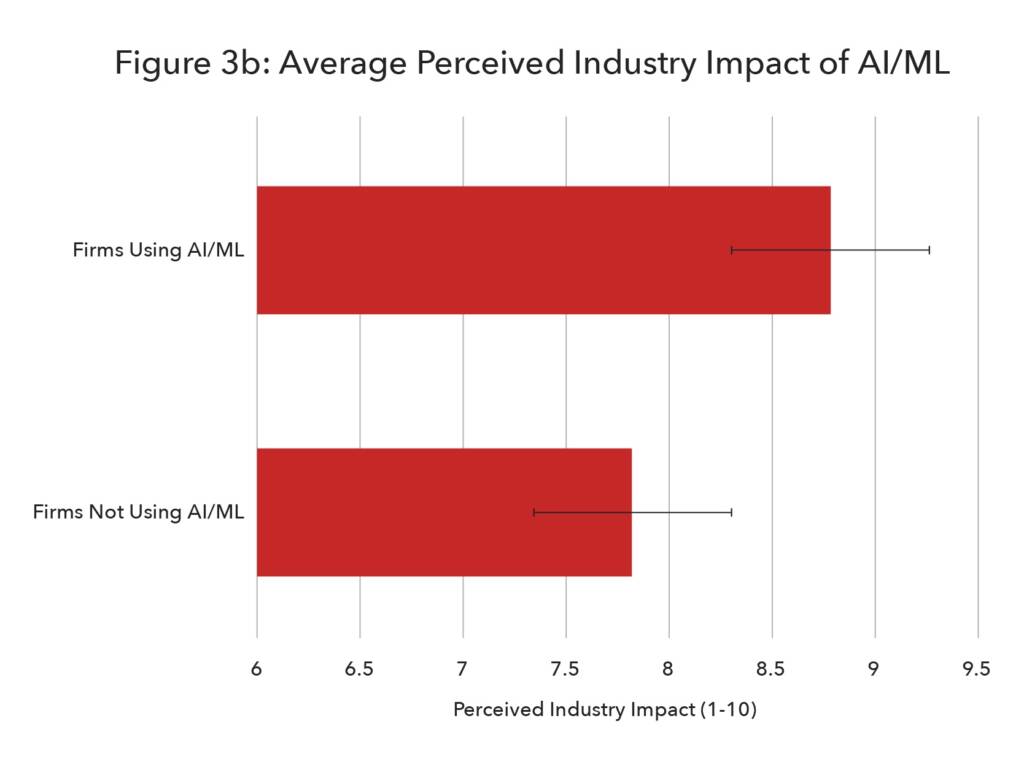
AI brings the power of data to the next stage compared to big data analytics. The ability of AI-powered programmes to parse and understand data has vast implications for financing processes. In addition, it has the capability to facilitate the creation of new processes that were simply too complicated to be done with the human brain itself, including predictive insights across trade functions. The development of predictive insight capabilities has interesting applications, such as credit scoring. A better outcome for credit scoring could help shift the focus towards good risk, potentially increasing MSME access to trade finance (which is low-risk by nature). At its core, AI has the power to go beyond the limited capabilities of human intelligence.
Use cases of AI
- There are multiple examples of companies using AI and ML to improve their financing solutions to the benefit of all, in particular MSMEs.
- For example, Efcom, a factoring software firm based in Germany, uses AI as a risk monitoring tool to determine if an invoice is fraudulent.
- QuantaVerse, for its part, uses AI for entity resolution and relationship-mapping and to monitor transactions for suspicious activity, which are all-important for the onboarding of new customers and financial crime compliance.
- Another firm that leverages AI to assist with client onboarding is Temenos. Temenos also uses AI to help banks conduct eligibility checks and process loan applications.
- RHB Banking Group has an AI-powered mobile app to help with compliance checking and personalized offerings.
- Other companies, such as Flowcast, a US-based AI firm, leverage machine learning methodologies to create predictive models that assess risk. Flowcast’s models render explainable a business’ creditworthiness, its risk of delinquency, its timeliness in making repayments, and the likelihood of dilution of its transactions.
- Ant Group, a member of the Alibaba Group, uses AI and data from mobile payment platform Alipay to run an extraordinary variety of businesses, including consumer lending, money market funds, and wealth management, health insurance and credit rating services. AI supplements Ant Group’s business functions on many fronts, including fraud prevention and risk profiling.
- Tradeteq is another fintech company that uses big data analytics and AI for credit scoring to help MSMEs which are often deemed “too risky” by current credit rating models to access finance. Tradeteq provides AI-powered predictive credit analytics to assess the riskiness of clients, vendors and individual transactions, and to assess the potential for defaults in trade finance liabilities of private and unrated companies.
- Finally, AI is also being used by companies for dynamic discounting and supply-chain financing.
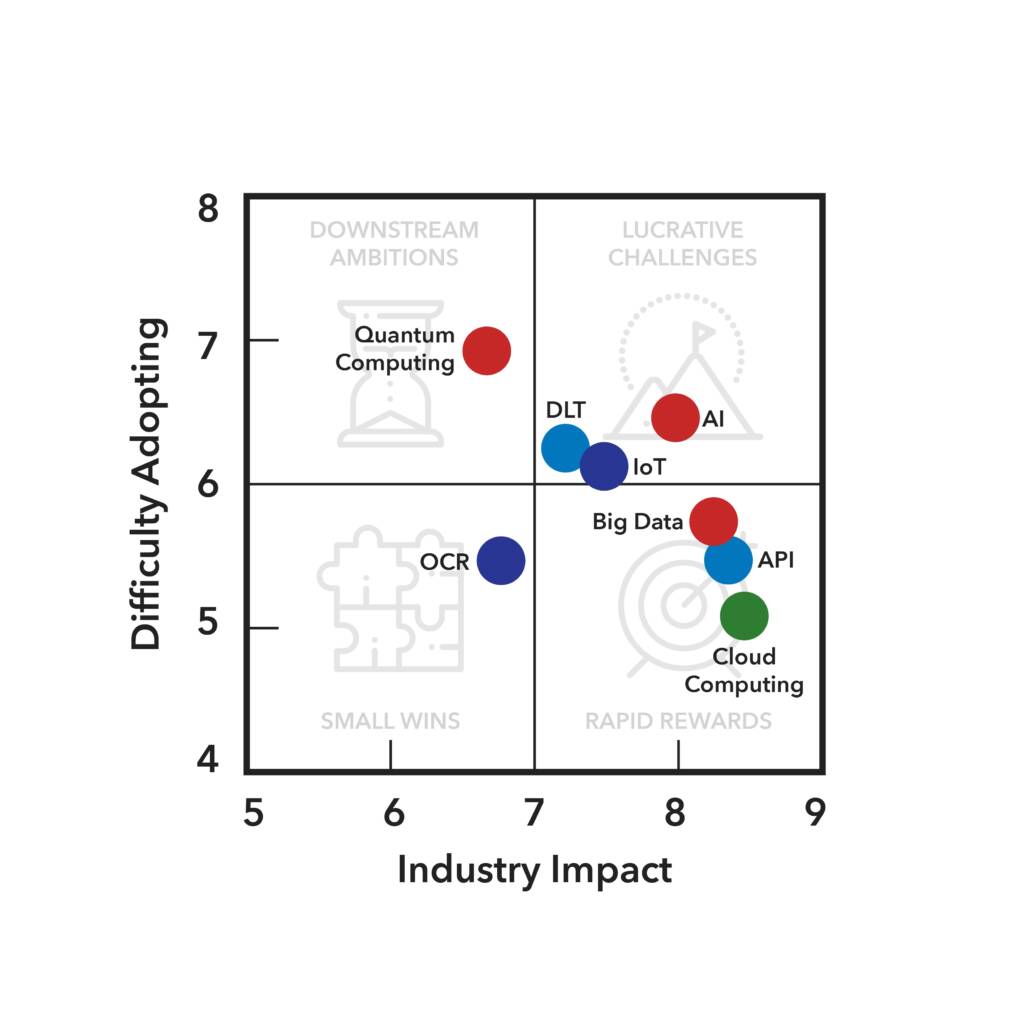
For more information about this diagram, visit our research methodology page.
Addressing AI challenges
While the road ahead for AI is promising, it is not without its challenges. The efficiencies of AI are maximized when applied to digitally native documents. Unfortunately, we are still facing regulatory challenges on the acceptance of digitally native documents. In most instances, trade transactions necessitate the use of paper documents, which AI tools in isolation are unable to access. If AI is to realize its full potential, outdated regulatory requirements will need to be updated and advancements will need to be made in other supporting technologies, namely optical character recognition (OCR). Unfortunately, OCR currently requires human intervention to ensure accuracy. The key in this instance is to bypass the error-prone middleman, OCR, entirely. Updating regulations to accept the use of digital original trade documents would facilitate an environment in which the entire trade cycle is paperless and can benefit from the power of digitalization.
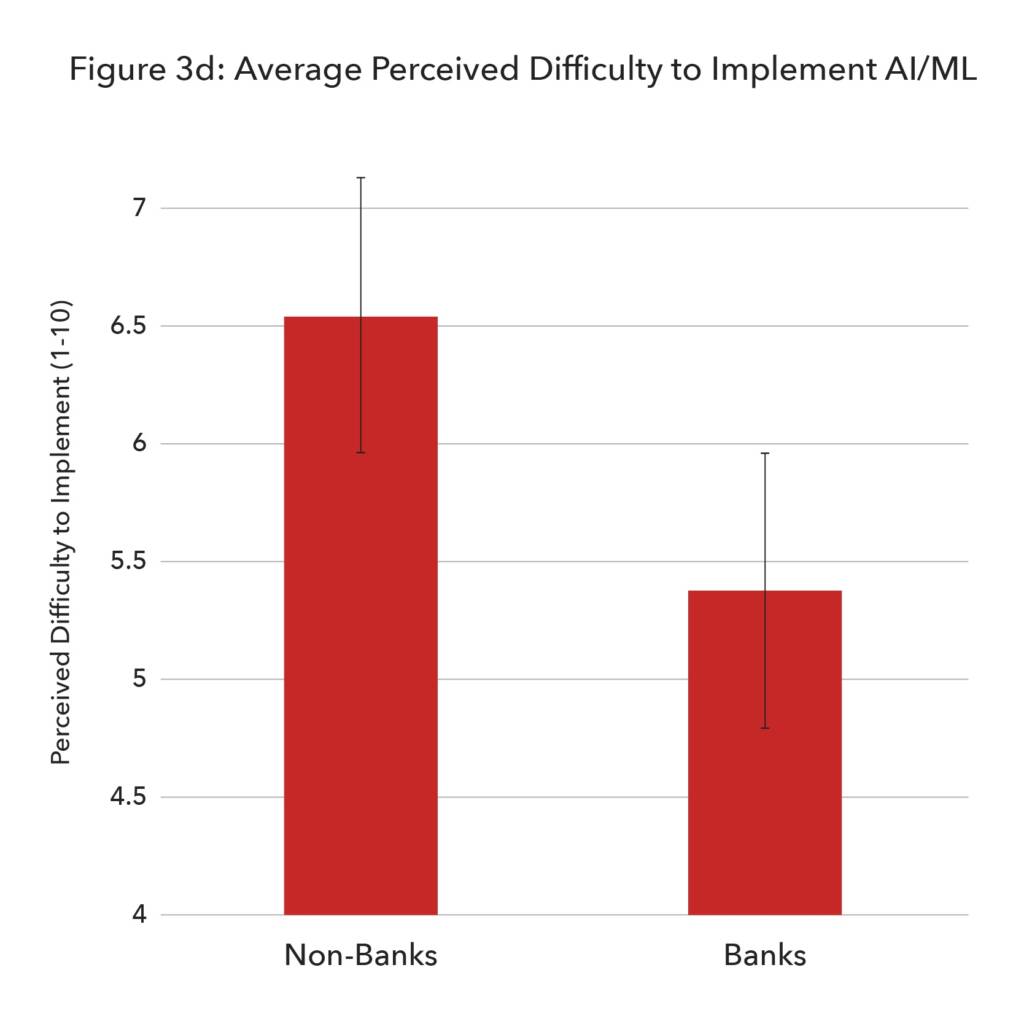
Most current national regulations do not allow most AI solutions to be widely adopted. This stems from legal concerns, such as the ambiguity of Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP) rules, which do not specify whether AI can be used in lieu of humans. As policymakers work to bring these regulations into the digital age, however, they must not do so using clauses that limit AI’s usefulness. It will be key that regulators do not require from machines too much compared to what they require from human beings, such as the explainability of underwriting decisions. Overburdening of this nature would set AI adoption back considerably.
Likewise, too much regulatory change poses a particular challenge for AI and ML. Machine learning is only as good as the input and supervision which can also be complicated by changing requirements and regulations. Changes to regulations, such as those used in compliance, will effectively require the algorithm to learn a whole new set of rules – a time-consuming and costly process.
Another major step forward for AI in trade finance will be the further standardization of trade documents and data formats. While AI models are able to decipher unstandardized forms better than previous computing technologies, standardized forms would lead to a higher recognition ratio and subsequently more accurate prediction models. Prediction model accuracy is a direct driver of the appetite for AI adoption.
Progress in education will help firms to make the decision to implement AI. Education on the usefulness of AI will allow banks to fully understand the benefits that using it to help small businesses will have for the sector. Explainable artificial intelligence (“XAI”), whereby the results of AI algorithms can be conveyed to and understood by humans, will provide further transparency.
Another crucial challenge to be addressed is that of the lack of trust of the human teams within financial institutions with regard to algorithms. Many employees feel threatened by algorithmic tools and fear that by assisting the machine, they will train themselves out of a job. To overcome this, firms seeking to implement the technology need to educate their employees both on its benefits and its limitations. Document checkers need to be trained to understand where the technology assists them, but also where it does not assist them, to prevent a mismatch of expectations. There is still a human checker involved, and this person needs to know what the machine is not able to pick up. It is the people that will give AI its power and they need to be prepared. This will prevent a mismatch of expectations and help employees to understand that these algorithms exist to enable, not to replace.
Publishing Partners
- Tradetech Resources
- All Tradetech Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences















