Blockchain & DLT for trade finance

Contents
Blockchain for Trade Finance
Welcome to our blockchain hub, a comprehensive guide by Trade Finance Global on the use of distributed ledger technologies (DLT) and blockchain within international trade, trade finance, and shipping.
Consortia, networks, and technologies have emerged in attempts to digitise trade, yet to date, their applications have been relatively unsuccessful and disjointed.
We investigate some of the key opportunities and challenges the in the current ecosystem, and take an in-depth look at what needs to happen for the industry to evolve.
Just as TCP/IP, HTML, and HTTP provide shared and open standards and protocols that enabled the internet to become what it is today, so too can blockchain and related technologies create a flatter, smarter, more connected, and overall better world for global trade and commerce.
Video – WTO and TFG Launch ‘Blockchain & DLT for Trade: Where do we stand?’
FAQ
Infographic: How does Blockchain work?
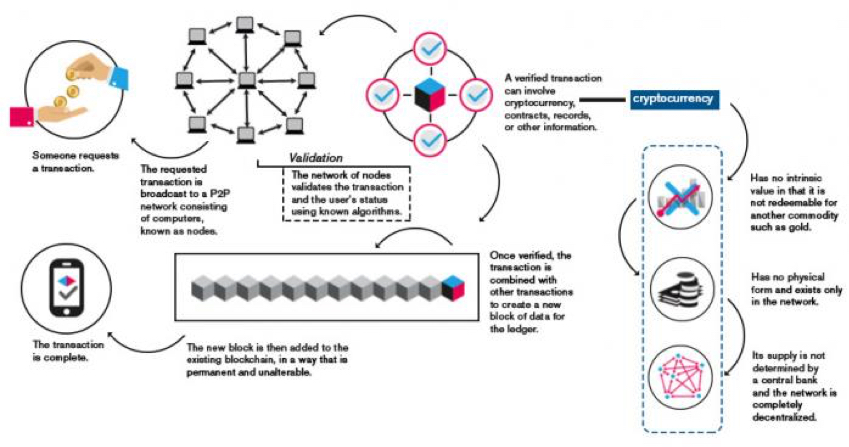
Source: By Shivratan rajvi [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], from Wikimedia Commons
Publishing Partners
- Blockchain & DLT Resources
- All Blockchain & DLT Topics
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Conferences
















