Prepayment Finance

Overview

Trade Finance without Barriers
Informing Today’s Market, Financing tomorrow’s Trade.
Get Trade FinanceContent
Producers often face funding issues especially in a country with exchange control regulations. Prepayment offers a simple solution to this predicament by enabling producers to receive advance payment for their commodities and goods.
Prepayments are the payments of bills, operating expenses/non-operating expense or settlement of debts, before their due dates.
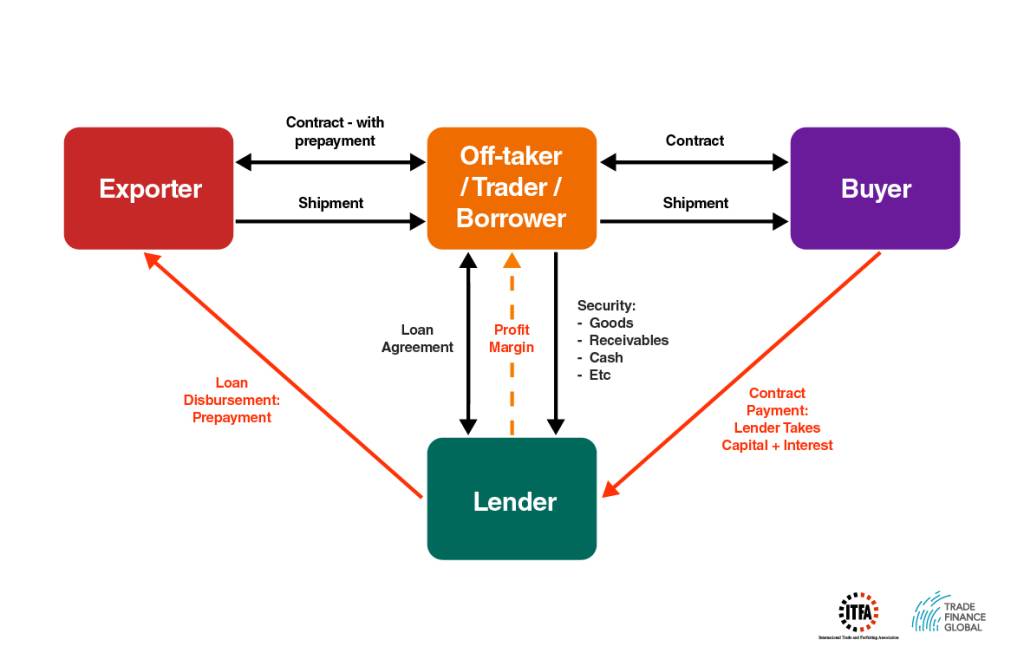
How does it work?
Signing a prepayment contract allows the borrowers to prepay for goods and assets provided by their producers. The parties involved sign a prepayment and an off-take agreement under which the borrower pays the money upfront. The seller uses the funds to produce goods and interest is applied on any left-over or outstanding amounts under this agreement. A typical prepayment finance deal includes an allocation of the lender’s rights under the prepayment contract and the buyer’s rights under the off-take contract. It is also possible for the security to be taken over the bank account and the goods into which the buyer makes the payment. The diagram below (Fig 1) illustrates how prepayment finance operates.
Diagram – Prepayment Finance
Other Types of Prepayment Finance
There are three main types of prepayment finance:
- Prepayments by individuals: Individuals can also make prepayments and the great thing about this is that the accounting process is considerably simpler. For instance, a customer might delay the payment of their credit card bill by 30 days. Let’s say a customer spends $2000 on his credit card and clears the bill that day. Even though, he made the payment shortly after using his credit card, it is still considered a prepayment because the bill isn’t really due for another 30 days.
- Prepayment by Corporations: Corporations pay for the costs of assets to be used in the future, in advance. This prepayment is labelled as a normal expenditure once the company starts using the purchased asset.
- Prepayment by Taxpayers: Taxpayers unknowingly make prepayments of taxes as some of their pay-check is stuck. Self-employed individuals, for example, are required to make the advance payment of taxes by making quarterly approximated tax payments. However, they receive a tax refund if they pay more than their actual tax liability.
Advantages of prepayment finance
- Enables seller of goods to successfully sign long term supply deals with producers in return for the provision of finance, funded by the buyer of product or commodities. This provides producers the financing they need to manufacture goods.
- Advance payment may also allow producers to search for further trade financing to expand its lending base and to diminish risks associated with funding.
- There is also the incentive of reduced interest payment on the left-over primary amount. In other words, if you are making a prepayment of any loans, your interest pay-out becomes smaller.
- Corporations can use the advance payments to pay their workforce and expenses.
- By refinancing the debt, individuals can pay past debt in advance.
Case Study
Duferco Group and HBIS Group Tangsteel Company
Duferco is an extremely varied and competent Group. Its main activities are in the Energy, Industrial and Shipping business sectors and they operate in 22 countries around the world. HBIS Group Tangsteel company is China’s large steel enterprise and one of the pillars of HBIS. It is located at the center of Bohai economic circle joining Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei.
In 2012, Duferco initiated a prepayment plan as part of its growing commercial and technical relationship with Tangsteel. Duferco was not only the exclusive off-taker of steel products exported but also a 10% risk guarantor under the signed agreement. The loan was facilitated by Deutsche Bank (China) Shanghai Branch whose trustees acted as security agents. Tangsteel used this prepayment steel loan to expand its international business.
Disadvantages of prepayment finance
- Prepayment tariff costs are higher than usual tariff costs because of the costs associated with serving customers through this method.
- Risks associated with deals can’t be completely eliminated and a trader is rarely permitted to transfer them to banks.
- Especially in commodities finance, there are more potential issues and risks around pre-paying a supplier and loans have to be closely monitored.














