Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development recently published the World Investment Report 2023 stating that foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to Africa reached the level of $45 billion in 2022, demonstrating Africa’s attractiveness as a destination for investment.
There are two primary factors for the recent surge in FDI:
- Africa is home to 30% of the world’s mineral reserves, which has drawn the attention of many investors. The continent’s vast reserves of natural resources provide opportunities for exploration, extraction, and export. Additionally, there has been an increase in investments in renewable energy in many African countries due to the natural exposure of Africa to both solar and hydro power.
- Africa’s population is rapidly growing, with 1.4 billion people, representing 17% of the world’s population. Furthermore, 60% of the continent’s population is below the age of 25. As a result, there is an increasing demand for essential services such as infrastructure, agriculture (Africa has 65% of the world’s arable land), education, and healthcare.
A notable emerging trend in various African countries is the governmental insistence on foreign investors incorporating a certain level of transformation of extracted natural resources within the country, ensuring a minimum added value is retained locally. This is expected to further augment FDI in Africa in the coming years.
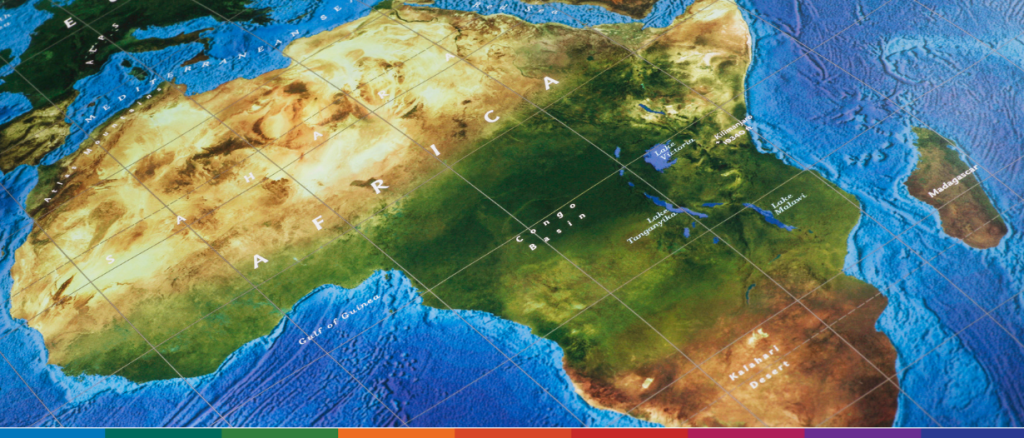
Nevertheless, discussions about Africa must acknowledge the considerable economic, legal, and cultural diversity among its regions. Understanding and integrating this diversity are pivotal for successful engagement and investment in the continent.
Considerations before investment
Investing in Africa presents a promising opportunity, but it is crucial to approach it with an understanding of cultural differences and to refrain from perceiving the local market solely through a foreign lens. This is a fundamental consideration to bear in mind before investing in the continent.
Practically, securing local support is imperative at various stages of the investment process:
- Choosing the right local partner is a pivotal factor for success. The ideal local partner should have the potential to unlock opportunities and streamline interactions with local administrations and clients, thereby significantly facilitating the overall business relationship.
- Collaborating with professionals well-versed in legal, tax, and other aspects of business development is crucial. These experts play a key role in conducting a comprehensive market study before committing to investments in Africa.
- Adopting a business model aligned with local costs is essential; profitability may be compromised if the investor attempts to generate local revenue with foreign costs, particularly in personnel expenses.
- Implementing a plan for knowledge transfer is equally vital. This not only helps in integration but also contributes to being recognized locally as a responsible company.
Local legal and tax systems: How to familiarise yourself
What steps should you take in order to become familiar with local legal and tax systems which vary greatly across the continent?
Significant efforts have been made by African multilateral institutions to harmonise commercial and tax laws.
An example of this is the Organisation for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa (OHADA), established in 1993. OHADA aims to increase legal certainty and facilitate foreign investment across West and Central Africa by harmonising business laws.
The harmonisation of laws promotes economic integration and globalisation of the economy, allowing investors to extend their investments across multiple African countries.
When investing in African countries, it’s crucial to be supported by local professionals who understand the local frameworks and international treaties.
It’s important to hire tax and legal advisors with international backgrounds, but with extensive knowledge of local frameworks and international treaties.
They should take the time to understand and study your business to deliver top-quality support with international standards. Additionally, staying updated with local legal and tax newsletters and maintaining periodic contact with local advisors through meetings is essential.
Integrating into a network of local business actors, such as chambers of commerce, employer syndicates, economic missions of embassies, and development agencies, can provide opportunities to exchange with other entrepreneurs and stay up-to-date with the latest developments.
Three steps before expanding into Africa
The first three essential steps for a business leader looking to expand their business in Africa would involve:
Market study: Conduct a comprehensive market study to understand the local consumer behaviour, demand for products or services, competition, and potential growth opportunities within the target African market.
Tax and legal study: Undertake a thorough examination of the local tax regulations, legal requirements, and international treaties related to investment protection, taxation, and customs. It’s crucial to ensure compliance with local laws and understand the implications of international agreements on business operations.
Prepare a solid business plan: Develop a well-structured business plan tailored to the specific African market, outlining the business activities, financial projections, operational strategies, and risk management. Controlling the budget and financial resources is vital for a successful expansion.
Don’t forget the regulator and financial aspects
Investment protection: Assess whether the investment is protected by any multilateral or international treaties currently in force within the target African country. Understanding the legal framework for investment protection is critical for mitigating risks.
Dividend and capital transfer: Evaluate the regulations and practicalities related to the transfer of dividends or the selling price of the company, ensuring that there are no obstacles to repatriating profits or capital.
Local currency trends: Analyse the trends and stability of the local currency to anticipate potential impacts on financial transactions, cash flow, and profitability.
Financing options: Explore and study the available financing options within the African market, including local banking institutions, investment funds, and government-supported initiatives. Additionally, consider the potential for financial support from the parent company or international sources.
 Australia
Australia Hong Kong
Hong Kong Japan
Japan Singapore
Singapore United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United States
United States France
France Germany
Germany Ireland
Ireland Netherlands
Netherlands United Kingdom
United Kingdom






Comments are closed.